Vulnerability
Management System
Vulnerability Management is a critical, continuous process in cybersecurity focused on identifying, prioritizing, and addressing security vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It’s designed to proactively defend against cyber threats by identifying weaknesses in systems, applications, networks, and devices before attackers can exploit them. Rather than a one-time solution, vulnerability management is an ongoing cycle that provides organizations with the insight needed to protect valuable assets, maintain compliance, and strengthen overall security posture.
Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Analysis:
- After vulnerabilities are identified, they are analyzed to determine their potential impact. This is done by examining the severity of each vulnerability, using scoring systems like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which rates vulnerabilities on a scale from low to critical. For instance, a vulnerability with a high CVSS score on a public-facing web application would demand immediate attention due to its risk of exposure.
Example of Vulnerability Management in Action
Imagine a retail company with an e-commerce website where customers enter sensitive information. During a routine vulnerability scan, the company identifies a critical vulnerability in its web server software, which has not yet been patched. This vulnerability could allow remote attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Velit expetendis omittantur sed ei, sit suavitate deseruisse sententiae ex. Ne omnium mentitum sea. Hinc interesset usu no, id nec autem quando sadipscing. Vix quem errem malorum et, elit labores reprehendunt ut usu. Nullam ornatus legimus est ei, denique intellegat ex est.
Mel meis equidem intellegebat te. Ut vix nostrud alienum vivendum. Cum ex alia legere ceteros. Eum torquatos rationibus ea. Cu mea postulant reprimique, modus aperiam dignissim nam an, duis porro repudiandae ne duo.
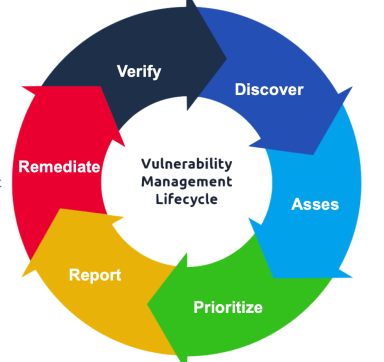
Key Steps in the Vulnerability Management Process
Asset Discovery and Prioritization:
- The first step is identifying and classifying all assets within the organization, such as servers, applications, databases, and endpoints. Each asset is assessed based on its criticality to the business, which helps in prioritizing remediation efforts. For example, a web server handling customer data would have a higher priority than a development server used for testing.
Vulnerability Scanning:
- Using automated scanning tools, vulnerabilities are identified across all assets. Tools such as Nessus, Qualys, or OpenVAS perform extensive scans to detect outdated software versions, misconfigurations, missing patches, and other weaknesses. Vulnerability scans can be customized for internal (inside the organization’s network) or external (from outside the network perimeter) use to cover all angles.
Prioritization and Remediation:
- Not all vulnerabilities require immediate action. Remediation strategies are based on factors like the asset’s importance, the vulnerability’s severity, and the current level of exposure. Common remediation methods include applying software patches, changing configurations, updating security controls, or isolating the vulnerable system. In cases where immediate remediation isn’t possible, temporary solutions like firewall rules or access control changes might mitigate the risk until a fix is deployed.
Verification and Monitoring:
- After remediation, another scan or assessment is performed to ensure that the vulnerability is fully resolved. Continuous monitoring is also essential, as new vulnerabilities emerge over time. Organizations need to implement regular scanning and keep up with new vulnerabilities through threat intelligence sources, ensuring they maintain a secure environment.
©Dacstech Copyright. All rights reserved.
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.
